Clinical-stage cannabinoid development company Incannex Healthcare (ASX: IHL) has received positive results from pre-clinical in vitro studies into the anti-inflammatory potency of its lead drug IHL-675A against sepsis-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome (SAARDS).
Various fixed doses of IHL-675A’s two key constituents – cannabidiol (CBD) and hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) – were used in the studies to assess the drug’s anti-inflammatory response. The combination drug was shown in the experiment to suppress the assessed inflammation biomarkers (cytokines) by greater than multiples of CBD.
Trial method
The trial involved human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) being stimulated with bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and then incubated with a range of CBD and HCQ concentrations.
The constituents were used in combination and alone, and then stimulated with LPS to induce an inflammatory response. The response was assessed by measuring the level of cytokines (inflammatory cell-signaling proteins) in the culture medium after 24 hours. A reduction in cytokine levels in response to drug treatment was deemed to be indicative of anti-inflammatory activity.
Cytokine inhibition
IHL-675A was shown to outperform cytokine inhibition of CBD by 109% to 767% after 24 hours from CBD’s administration. The combined CBD-HCQ dosage outperformed the predicted cytokine inhibition by 87% to 767% after the same period.
Incannex managing director and chief executive officer Joel Latham said the CBD and HCQ “acted synergistically” to inhibit production of the assessed inflammatory cytokines.
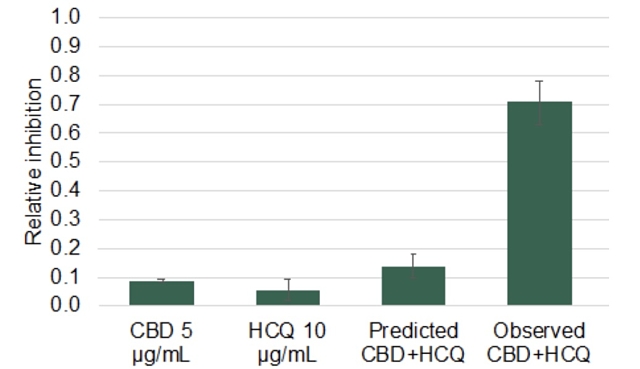
In particular, Incannex provided data from its experiment on the effect of IHL-675A on IL-6, a cytokine that received media attention as a biomarker of interest during the COVID-19 crisis.
Expanded Provisional Patents
Incannex has sought patent protection on the CBD-HCQ combination due to potential implications in the treatment of SAARDS, which is a hyper-inflammatory response to infections and the leading cause of mortality in patients who have contracted the COVID-19 virus.
As a result of the test, however, Incannex has expanded its provisional patent protection to cover a range of other inflammatory diseases that it says represent potential additional opportunities for the company.
Mr Latham said that Incannex will continue to assess the benefit of IHL-675A over CBD-only treatments in future studies.
“As a company, we set out to gain evidence that our proprietary combination of CBD and HCQ would exhibit significant synergistic outperformance against the individual constituents.”
“Not only have we managed to achieve this, but we have significantly outperformed against our predictions of anti-inflammatory activity in the IHL-675A combination drug. Potentially, this could mean that IHL-675A is a better alternative to CBD oil products for inflammatory diseases, subject to further examination,” Mr Latham added.
No registered treatments for SAARDS
SAARDS is a type of severe respiratory failure for which there is no treatment available using an approved pharmaceutical agent.
The condition is typically treated in an intensive care unit using mechanical ventilation and oxygen supplementation.
Mechanical ventilation is usually delivered through a rigid tube which enters the oral cavity and is secured in the airway, or by tracheostomy when prolonged ventilation is necessary.
Survival rates for acute respiratory distress syndrome vary depending on age, the underlying cause of the illness, co-morbidities and other factors.
Some studies estimate the mortality rate for patients to be between 36% and 52%.
